Static NAT46 <> NAT64, why we need both and they’re part of NAT-PT
Sometime ago I came across a requirement for the ability to deal with IPv4 conflicts during M&A and/ or MSPs taking on another customer who happened to be using an existing customers IPv4 subnet.
After doing some research and help from colleagues at the time, the following solution was created using Juniper SRX devices.
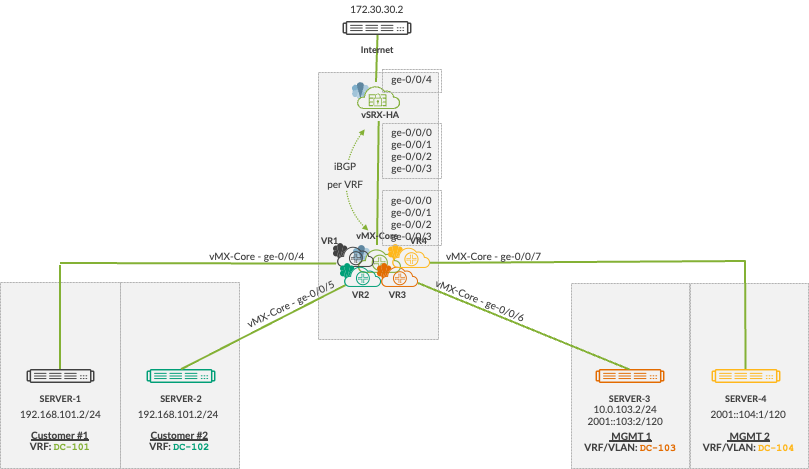
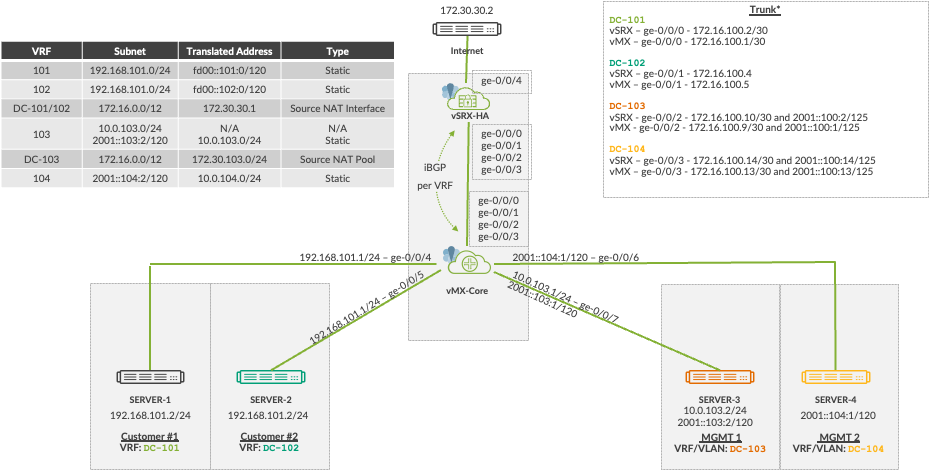
The example below uses a vMX to separate the networks and using routing-instances and dedicated interfaces per routing-instance up to the vSRX.
Lab Topology
Objectives
In Scope
Provide secure routing between NOC/ management subnet(s) and the individual customers.
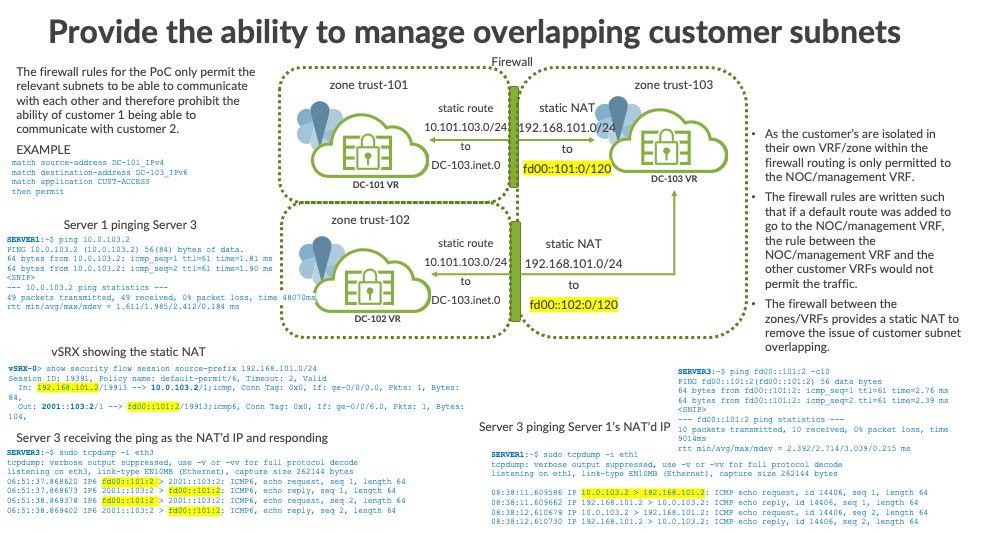
Provide the ability to manage overlapping customer subnets using static NAT IPv4 to private IPv6.
Prevent customer networks from communicating with each other.
Out of Scope
Hardening the SRX.
How to resolve the issue of, the NOC/ management subnet(s) overlap with the customer subnet.
Explicitly preventing the NOC/management IPv4 subnet(s) communicating with the customer IPv4 subnets, even if the customer IPv4 subnets overlap.
Routing for an alternative/backup default gateway in the customer network(s).
Configuration and support of the SRX’s IDP capabilities.
How to configure an SRX for HA.
Configuring DNS ALG for NAT-PT.
Assumptions
The NOC/management subnet(s) will:
not overlap with the customer subnet.
will only need the following access to the customers subnets:
SSH.
SNMP.
PING/ICMP (Ipv4 and IPv6).
The customer subnets will only need access to the NOC/management subnet(s) for:
AAA services (TACACs and RDP).
NTP.
PING/ICMP (Ipv4 and IPv6).
The SRX will be the default gateway for all VRFs.
Dependencies
The SRX has to be in ‘flow-based’ mode for IPv4 and IPv6 and rebooted before any of the below commands are used:
The IPv6 subnet cannot be smaller than the IPv4 subnet it’s being mapped to .
The application-identification has to be installed before any of the below commands are used:
Check to see what is installed - https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/application-identification/topics/ref/command/show-services-application-identification-application.html or https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/cli/topics/ref/command/show-groups-junos-defaults.html.
So How Does It Work?
Packet Walk
Steps
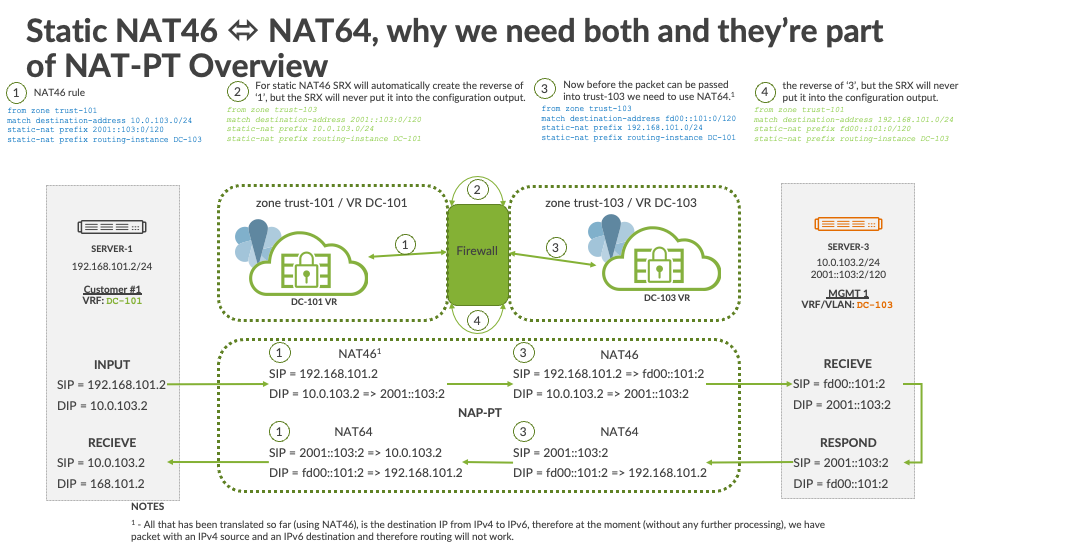
NAT46 rule
For static NAT46 SRX will automatically create the reverse of step 1, but the SRX will never put it into the configuration output.
Now before the packet can be passed into trust-103 we need to use NAT641.
The reverse of step 3, but the SRX will never put it into the configuration output.
Configlets
Step 1
from zone trust-101
match destination-address 10.0.103.0/24
static-nat prefix 2001::103:0/120
static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-103Step 2
from zone trust-103
match destination-address 2001::103:0/120
static-nat prefix 10.0.103.0/24
static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-101Step 3
from zone trust-103
match destination-address fd00::101:0/120
static-nat prefix 192.168.101.0/24
static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-101Step 4
from zone trust-101
match destination-address 192.168.101.0/24
static-nat prefix fd00::101:0/120
static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-103Sandbox Topology
Working Examples
IPv4 flows verification
Confirm the firewall rule(s) and the action for a packet type:
vSRX-DC# run show security match-policies source-ip 192.168.101.2 destination-ip 2001::103:2 source-port 1 destination-port 1 protocol icmp from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-103
Policy: default-permit, action-type: permit, State: enabled, Index: 6
0
Policy Type: Configured
Sequence number: 1
From zone: trust-101, To zone: trust-103
Source vrf group:
any
Destination vrf group:
any
Source addresses:
DC-101_IPv4(global): 192.168.101.0/24
Destination addresses:
DC-103_IPv6(global): 2001::103:0/120
Application: CUST-ACCESS
IP protocol: icmp, ALG: 0, Inactivity timeout: 60
ICMP Information: type=255, code=0
IP protocol: 58, ALG: 0, Inactivity timeout: 60
ICMP Information: type=255, code=0
IP protocol: tcp, ALG: 0, Inactivity timeout: 1800
Source port range: [0-0]
Destination ports: 3389
IP protocol: tcp, ALG: 0, Inactivity timeout: 1800
Source port range: [0-0]
Destination ports: 49
IP protocol: tcp, ALG: 0, Inactivity timeout: 1800
Source port range: [0-0]
Destination ports: 65
Per policy TCP Options: SYN check: No, SEQ check: No, Window scale: NoHost to Host Communication Verification
DC-101 to DC-103
Ping from SERVER-1 in DC-101 to SERVER-3 in DC-103
ubuntu:~$ ping 192.168.103.2 -c 100
PING 192.168.103.2 (192.168.103.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.103.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=2.45 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.103.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=2.45 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.103.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=2.45 ms
.... <SNIP>
--- 192.168.103.2 ping statistics ---
100 packets transmitted, 100 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 2.455/2.455/2.455/0.000 msVerify the session flow creation to static NAT address2:
vSRX-HA> show security flow session source-prefix 192.168.101.0/24 extensive
Session ID: 12607, Status: Normal
Flags: 0x4000000/0x0/0x2/0x2000003
Policy name: default-permit/6
Source NAT pool: Null
Dynamic application: junos:UNKNOWN,
Encryption: Unknown
Url-category: Unknown
Application traffic control rule-set: INVALID, Rule: INVALID
Maximum timeout: 60, Current timeout: 2
Session State: Valid
Start time: 165580, Duration: 3
In: 192.168.101.2/17189 --> 10.0.103.2/15;icmp,
Conn Tag: 0x0, Interface: ge-0/0/4.0,
Session token: 0x700a, Flag: 0x621
Route: 0xf0010, Gateway: 172.16.100.1, Tunnel ID: 0, Tunnel type: None
Port sequence: 0, FIN sequence: 0,
FIN state: 0,
Pkts: 1, Bytes: 84
Out: 2001::103:2/15 --> fd00::101:2/17189;icmp6,
Conn Tag: 0x0, Interface: ge-0/0/7.0,
Session token: 0x900c, Flag: 0x622
Route: 0x130010, Gateway: 2001::100:1, Tunnel ID: 0, Tunnel type: None
Port sequence: 0, FIN sequence: 0,
FIN state: 0,
Pkts: 1, Bytes: 104
Total sessions: 1Note: Check the byte size on the return session to make sure they match in the return direction.
How SERVER-3 in DC-103 sees the ping request from SERVER-1 in DC-101:
ubuntu:~$ sudo tcpdump -i eth3
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on eth3, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
06:51:37.868620 IP6 fd00::101:2 > 2001::103:2: ICMP6, echo request, seq 1, length 64
06:51:37.868673 IP6 2001::103:2 > fd00::101:2: ICMP6, echo reply, seq 1, length 64DC-103 to DC-101
Ping from SERVER-3 in DC-103 to SERVER-1 in DC-101:
root@ubuntu:~# ping fd00::101:2 -c100
PING fd00::101:2(fd00::101:2) 56 data bytes
64 bytes from fd00::101:2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=2.67 ms
64 bytes from fd00::101:2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=2.67 ms
64 bytes from fd00::101:2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=2.67 ms
... <SNIP>
--- fd00::101:2 ping statistics ---
100 packets transmitted, 100 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 2.613/2.613/2.613/0.000 msVerify the session flow creation to static NAT address3:
vSRX-DC> show security flow session source-prefix 2001::103:0/120 extensive
Session ID: 12757, Status: Normal
Flags: 0x84000000/0x0/0x2/0x2800003
Policy name: default-permit/12
Source NAT pool: Null
Dynamic application: junos:UNKNOWN,
Encryption: Unknown
Url-category: Unknown
Application traffic control rule-set: INVALID, Rule: INVALID
Maximum timeout: 4, Current timeout: 2
Session State: Valid
Start time: 168194, Duration: 2
In: 2001::103:2/17083 --> fd00::101:2/1;icmp6,
Conn Tag: 0x0, Interface: ge-0/0/7.0,
Session token: 0x900c, Flag: 0x623
Route: 0x130010, Gateway: 2001::100:1, Tunnel ID: 0, Tunnel type: None
Port sequence: 0, FIN sequence: 0,
FIN state: 0,
Pkts: 1, Bytes: 104
Out: 192.168.101.2/1 --> 10.0.103.2/17083;icmp,
Conn Tag: 0x0, Interface: ge-0/0/4.0,
Session token: 0x700a, Flag: 0x620
Route: 0xf0010, Gateway: 172.16.100.1, Tunnel ID: 0, Tunnel type: None
Port sequence: 0, FIN sequence: 0,
FIN state: 0,
Pkts: 1, Bytes: 84
Total sessions: 1How SERVER-1 in DC-101 sees the ping request from SERVER-3 in DC-103
root@ubuntu:~# tcpdump -i eth1
[sudo] password for jcluser:
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on eth1, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
07:33:47.126039 IP 10.0.103.2 > 192.168.101.2: ICMP echo request, id 17080, seq 1, length 64
07:33:47.126092 IP 192.168.101.2 > 10.0.103.2: ICMP echo reply, id 17080, seq 1, length 64Sandbox Preparation
Linux Hosts Configuration
Configure each Ubuntu server IP address and static route:
# Server-1
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
eth1:
addresses:
- 192.168.101.2/24
routes:
- to: 192.168.0.0/16
via: 192.168.101.1
- to: 172.16.0.0/12
via: 192.168.101.1
# Server-2
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
eth2:
addresses:
- 192.168.101.2/24
routes:
- to: 192.168.0.0/16
via: 192.168.101.1
- to: 172.16.0.0/12
via: 192.168.101.1
# Server-3
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
eth3:
addresses:
- 192.168.103.2/24
- 2001::103:2/120
routes:
- to: 192.168.0.0/16
via: 192.168.103.1
- to: 10.0.0.0/8
via: 192.168.103.1
- to: 172.16.0.0/12
via: 192.168.103.1
- to: 2001::100:0/122
via: 2001::103:1
- to: fd00::/8
via: 2001::103:1
# Server-4
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
eth4:
addresses:
- 2001::104:2/120
routes:
- to: 2001::100:0/122
via: 2001::104:1
- to: fd00::/8
via: 2001::104:1Configure each Ubuntu servers to access the ‘Internet’ via the vSRX with:
# Internet-Server
nmcli -p dev
ifconfig eth1
sudo ip route add 172.16.0.0/12 via 172.30.30.1
sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
DEVICE="eth1"
ONBOOT=yes
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR=172.30.30.2
NETMASK=255.255.255.252
systemctl restart networkvMX and vSRX Configuration
vMX
vMX Ifd Configuration
Create the interfaces between the vMX and Linux hosts, and the vMX and the vSRX:
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 description SRX_ge-0/0/0_DC-101
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.100.1/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 description SRX_ge-0/0/5_DC-102
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.100.5/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 description SRX_ge-0/0/6_DC-103
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.100.9/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001::100:1/125
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 description SRX_ge-0/0/7_DC-104
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.100.13/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001::100:13/125
set interfaces ge-0/0/4 description SERVER1
set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.101.1/24
set interfaces ge-0/0/5 description SERVER2
set interfaces ge-0/0/5 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.101.1/24
set interfaces ge-0/0/6 description SERVER3
set interfaces ge-0/0/6 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.103.1/24
set interfaces ge-0/0/6 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001::103:1/120
set interfaces ge-0/0/7 description SERVER4
set interfaces ge-0/0/7 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.104.1/24
set interfaces ge-0/0/7 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001::104:1/120
vMX Routing-Instance VRF Configuration
Create a Routing-Instance VRF and create a BGP session per VRF towards vSRX4:
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 type internal
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 local-address 172.16.100.1
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 family inet unicast
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 export DIRECT
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 neighbor 172.16.100.2
set routing-instances DC-101 instance-type vrf
set routing-instances DC-101 interface ge-0/0/0.0
set routing-instances DC-101 interface ge-0/0/4.0
set routing-instances DC-101 route-distinguisher 100:65001
set routing-instances DC-101 vrf-target target:100:100
set routing-instances DC-101 vrf-table-label
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 type internal
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 local-address 172.16.100.5
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 family inet unicast
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 export DIRECT
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 neighbor 172.16.100.6
set routing-instances DC-102 instance-type vrf
set routing-instances DC-102 interface ge-0/0/1.0
set routing-instances DC-102 interface ge-0/0/5.0
set routing-instances DC-102 route-distinguisher 200:65001
set routing-instances DC-102 vrf-target target:200:200
set routing-instances DC-102 vrf-table-label
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 type internal
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 local-address 172.16.100.9
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 family inet unicast
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 export DIRECT
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 neighbor 172.16.100.10
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 type internal
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 local-address 2001::100:1
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 family inet6 unicast
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 export DIRECT-INET6
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 neighbor 2001::100:2
set routing-instances DC-103 instance-type vrf
set routing-instances DC-103 interface ge-0/0/2.0
set routing-instances DC-103 interface ge-0/0/6.0
set routing-instances DC-103 route-distinguisher 300:65001
set routing-instances DC-103 vrf-target target:300:300
set routing-instances DC-103 vrf-table-label
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 type internal
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 local-address 172.16.100.13
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 family inet unicast
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 export DIRECT
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 neighbor 172.16.100.14
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 type internal
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 local-address 2001::100:13
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 family inet6 unicast
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 export DIRECT-INET6
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 neighbor 2001::100:14
set routing-instances DC-104 instance-type vrf
set routing-instances DC-104 interface ge-0/0/3.0
set routing-instances DC-104 interface ge-0/0/7.0
set routing-instances DC-104 route-distinguisher 400:65001
set routing-instances DC-104 vrf-target target:400:400
set routing-instances DC-104 vrf-table-label
set routing-options autonomous-system 65535vMX Route Filters
Advertise direct addresses only with a route-filter:
set policy-options policy-statement DIRECT term DIRECT from protocol direct
set policy-options policy-statement DIRECT term DIRECT from route-filter 192.168.101.0/24 exact
set policy-options policy-statement DIRECT term DIRECT from route-filter 192.168.103.0/24 exact
set policy-options policy-statement DIRECT term DIRECT then accept
set policy-options policy-statement DIRECT-INET6 term DIRECT from protocol direct
set policy-options policy-statement DIRECT-INET6 term DIRECT from route-filter 2001::103:0/120 exact
set policy-options policy-statement DIRECT-INET6 term DIRECT from route-filter 2001::104:0/120 exact
set policy-options policy-statement DIRECT-INET6 term DIRECT then acceptvSRX
vSRX Ifd Configuration
Create the interfaces between the vSRX and the vMX:
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 description TO-DC-101
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.100.2/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 description TO-DC-102
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.100.6/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 description TO-DC-103
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.100.10/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001::100:2/125
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 description TO-DC-104
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.100.14/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001::100:14/125
set interfaces ge-0/0/4 description TO-INTERNET
set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 0 family inet address 172.30.30.1/30
vSRX Routing-Instance VRF Configuration
Routing-instance VR configuration and BGP session towards vMX. Each VR with default route which serves 2 purposes:
Advertise default route to vMX.
Route leak to default for internet traffic5.
set routing-instances DC-101 routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-table inet.0
set routing-instances DC-101 routing-options static route 10.0.103.0/24 next-table DC-103.inet.0
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 type internal
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 local-address 172.16.100.2
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 family inet unicast
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 export PER-VR-ADV
set routing-instances DC-101 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-101 neighbor 172.16.100.1
set routing-instances DC-101 interface ge-0/0/0.0
set routing-instances DC-101 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances DC-102 routing-options static route 10.0.103.0/24 next-table DC-103.inet.0
set routing-instances DC-102 routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-table inet.0
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 type internal
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 local-address 172.16.100.6
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 family inet unicast
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 export PER-VR-ADV
set routing-instances DC-102 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-102 neighbor 172.16.100.5
set routing-instances DC-102 interface ge-0/0/1.0
set routing-instances DC-102 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances DC-103 routing-options rib DC-103.inet6.0 static route ::/0 discard
set routing-instances DC-103 routing-options rib DC-103.inet6.0 static route 2001::104:0/122 next-table DC-104.inet6.0
set routing-instances DC-103 routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-table inet.0
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 type internal
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 local-address 172.16.100.10
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 family inet unicast
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 export PER-VR-ADV
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-103 neighbor 172.16.100.9
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 type internal
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 local-address 2001::100:2
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 family inet6 unicast
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 export PER-VR-ADV-INET6
set routing-instances DC-103 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-101 neighbor 2001::100:1
set routing-instances DC-103 interface ge-0/0/2.0
set routing-instances DC-103 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-instances DC-104 routing-options rib DC-104.inet6.0 static route ::/0 discard
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 type internal
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 local-address 172.16.100.14
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 family inet unicast
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 export PER-VR-ADV
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv4-104 neighbor 172.16.100.13
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 type internal
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 local-address 2001::100:14
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 family inet6 unicast
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 export PER-VR-ADV-INET6
set routing-instances DC-104 protocols bgp group ibgp-ipv6-104 neighbor 2001::100:13
set routing-instances DC-104 interface ge-0/0/3.0
set routing-instances DC-104 instance-type virtual-router
set routing-options autonomous-system 65535vSRX VRF to VRF Access
vSRX Security Zones
Create the security zones with:
set security zones security-zone untrust screen untrust-screen
set security zones security-zone untrust host-inbound-traffic protocols bgp
set security zones security-zone untrust interfaces ge-0/0/4.0
set security zones security-zone trust-101 tcp-rst
set security zones security-zone trust-101 host-inbound-traffic protocols bgp
set security zones security-zone trust-101 host-inbound-traffic system-services ping
set security zones security-zone trust-101 interfaces ge-0/0/0.0
set security zones security-zone trust-102 tcp-rst
set security zones security-zone trust-102 host-inbound-traffic protocols bgp
set security zones security-zone trust-102 host-inbound-traffic system-services ping
set security zones security-zone trust-102 interfaces ge-0/0/1.0
set security zones security-zone trust-103 tcp-rst
set security zones security-zone trust-103 host-inbound-traffic protocols bgp
set security zones security-zone trust-103 host-inbound-traffic system-services ping
set security zones security-zone trust-103 interfaces ge-0/0/2.0
set security zones security-zone trust-104 tcp-rst
set security zones security-zone trust-104 host-inbound-traffic protocols bgp
set security zones security-zone trust-104 host-inbound-traffic system-services ping
set security zones security-zone trust-104 interfaces ge-0/0/3.0
vSRX ‘Internet’ Access Security Policies
Allow the VRFs access to the ‘Internet’ with:
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match source-address any
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match destination-address any
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match application any
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone untrust policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match source-address any
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match destination-address any
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match application any
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone untrust policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match source-address any
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match destination-address any
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match application any
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone untrust policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match source-address any
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match destination-address any
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone untrust policy default-permit match application any
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone untrust policy default-permit then permit
vSRX MGMT Access
Create security policies between MGMT VR and Customer VRs6 with:
set security address-book global address DC-101_IPv4 192.168.101.0/24
set security address-book global address DC-102_IPv4 192.168.101.0/24
set security address-book global address DC-103_IPv4 10.0.103.0/24
set security address-book global address DC-103_IPv6 2001::103:0/120
set security address-book global address DC-104_IPv6 2001::104:0/120
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-103 policy default-permit match source-address DC-101_IPv4
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-103 policy default-permit match destination-address DC-103_IPv6
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-103 policy default-permit match application CUST-ACCESS
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-103 policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-104 policy default-permit match source-address DC-101_IPv4
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-104 policy default-permit match destination-address DC-104_IPv6
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-104 policy default-permit match application CUST-ACCESS
set security policies from-zone trust-101 to-zone trust-104 policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone trust-103 policy default-permit match source-address DC-102_IPv4
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone trust-103 policy default-permit match destination-address DC-103_IPv6
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone trust-103 policy default-permit match application CUST-ACCESS
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone trust-103 policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone trust-104 policy default-permit match source-address DC-102_IPv4
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone trust-104 policy default-permit match destination-address DC-104_IPv6
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone trust-104 policy default-permit match application CUST-ACCESS
set security policies from-zone trust-102 to-zone trust-104 policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone trust-101 policy default-permit match source-address DC-103_IPv6
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone trust-101 policy default-permit match destination-address DC-101_IPv4
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone trust-101 policy default-permit match application NOC-MGMT
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone trust-101 policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone trust-102 policy default-permit match source-address DC-103_IPv6
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone trust-102 policy default-permit match destination-address DC-102_IPv4
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone trust-102 policy default-permit match application NOC-MGMT
set security policies from-zone trust-103 to-zone trust-102 policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone trust-101 policy default-permit match source-address DC-104_IPv6
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone trust-101 policy default-permit match destination-address DC-101_IPv4
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone trust-101 policy default-permit match application NOC-MGMT
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone trust-101 policy default-permit then permit
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone trust-102 policy default-permit match source-address DC-104_IPv6
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone trust-102 policy default-permit match destination-address DC-102_IPv4
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone trust-102 policy default-permit match application NOC-MGMT
set security policies from-zone trust-104 to-zone trust-102 policy default-permit then permitvSRX Source NAT
DC-101 and DC-102 to Internet
set security nat source rule-set DC-101-INTERNET-RS from zone trust-101
set security nat source rule-set DC-101-INTERNET-RS to zone untrust
set security nat source rule-set DC-101-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-1 match source-address 192.168.101.0/24
set security nat source rule-set DC-101-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-1 match destination-address 0.0.0.0/0
set security nat source rule-set DC-101-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-1 then source-nat interface
set security nat source rule-set DC-102-INTERNET-RS from zone trust-102
set security nat source rule-set DC-102-INTERNET-RS to zone untrust
set security nat source rule-set DC-102-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-1 match source-address 192.168.101.0/24
set security nat source rule-set DC-102-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-1 match destination-address 0.0.0.0/0
set security nat source rule-set DC-102-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-1 then source-nat interfaceDC-103 pool to Internet
It is assumed that DC-104 doesn’t need access to the internet.
set security nat source pool DC-103-PUBLIC address 172.30.103.0/24
set security nat source rule-set DC-103-INTERNET-RS from zone trust-103
set security nat source rule-set DC-103-INTERNET-RS to zone untrust
set security nat source rule-set DC-103-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-2 match source-address 192.168.103.0/24
set security nat source rule-set DC-103-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-2 match destination-address 0.0.0.0/0
set security nat source rule-set DC-103-INTERNET-RS rule internet-rule-2 then source-nat pool DC-103-PUBLICvSRX Static IPv4 (NAT46) and IPv6 (NAT64) NAT
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 from zone [ trust-101 trust-102 ]
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-1 match destination-address 10.0.103.0/24
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-1 then static-nat prefix 2001::103:0/120
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-1 then static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-103
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-2 match destination-address 10.0.104.0/24
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-2 then static-nat prefix 2001::104:0/120
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-2 then static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-104
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 from zone [ trust-103 trust-104 ]
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-1 match destination-address fd00::101:0/120
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-1 then static-nat prefix 192.168.101.0/24
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-1 then static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-101
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-2 match destination-address fd00::102:0/120
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-2 then static-nat prefix 192.168.101.0/24
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-2 then static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-102Appendices
Address Book and Address-Set
To keep the policies light address-set’s can be used to group several address book entries together - https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/security-policies/topics/topic-map/security-address-books-sets.html.
High Availability for SRX
1. SRX HA Configuration Generator - https://support.juniper.net/support/tools/srxha/.
2. Configuring Chassis Clustering on SRX Series Devices - https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/chassis-cluster-security-devices/topics/topic-map/security-chassis-cluster-verification.html.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDP) Links
1. How to configure IDP on the SRX Series -
a. SRX Getting Started - Install license for Antivirus, Web Filter, IDP, or Antispam - http://kb.juniper.net/KB16675.
2. Juniper vSRX: Advanced Security Feature Demo -
3. Juniper SRX NGFW Walkthrough -
SRX Pre-Defined Applications and Address Books
Address Book - https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/security-policies/topics/topic-map/security-address-books-sets.html.
Pre-defined applications - https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/security-policies/topics/topic-map/policy-predefined-applications.html, (also see Dependencies).
Traffic Processing on SRX Series
Traffic Processing on SRX Series Devices Overview - https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/flow-packet-processing/topics/topic-map/security-srx-devices-processing-overview.html.
SRX Static NAT46 <=> NAT64, why we need both and they’re part of NAT-PT Overview
There are several Juniper documents covering this topic, but they don’t quite cover the use case of this PoC. The requirement of the PoC is to translate any IPv4 address to an IPv6 address, but keep the last octet the same, i.e., 192.168.101.2 becomes fd00::101:2, therefore a static NAT will be used.
As the SRX is stateful, static NATs automatically create the reverse rule in the SRX, but never display it in the configuration. That allows for a more condensed rule base in the SRX. However, the need for NAT-PT is that, as the IP address translated using NAT46 only the destination IP has been translated IPv4 to IPv6, therefore at thew moment (without any further processing), we have a packet with an IPv4 source and an IPv6 destination and therefore routing will not work. Therefore, we need a NAT64 rule to complete the source IP translation; hence NAT-PT.
Example
The ‘forward’ NAT46 rule from the NOC Management zone/VR to the customer zone/VR:
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 from zone trust-101
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-1 match destination-address 10.0.103.0/24
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-1 then static-nat prefix 2001::103:0/120
set security nat static rule-set NAT46 rule rule-1 then static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-103From this ‘forward’ NAT46 rule, we map anything that is originated in DC-103 VR (zone trust-103) from the IP subnet 2001::103:0/120, NAT it to IP subnet 10.0.103.0/24, and put the NAT’d traffic into zone trust-101 (DC-101 VR).
The ‘reverse’ NAT64 rule from the customer zone/ VR to the NOC Management zone/ VR:
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 from zone trust-103
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-1 match destination-address fd00::101:0/120
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-1 then static-nat prefix 192.168.101.0/24
set security nat static rule-set NAT64 rule rule-1 then static-nat prefix routing-instance DC-101From this ‘reverse’ NAT64 rule, we map anything that is originated in DC-101 VR (zone trust-101) from the IP subnet 192.168.101.0/24, NAT it to IP subnet fd00::101:0/120, and put the NAT’d traffic into zone trust-103 (DC-103 VR).
Links
Configuring NAT46 on SRX devices - https://kb.juniper.net/InfoCenter/index?page=content&id=KB33559&actp=METADATA.
All that has been translated so far (using NAT46), is the destination IP from IPv4 to IPv6, therefore at the moment (without any further processing), we have packet with an IPv4 source and an IPv6 destination and therefore routing will not work.
VRF table label RD and RT are for reference only and are only locally significant to the vMX
Each VR configured with static route with next-table to leak between VR
The rules defined here are based on the outline in the Assumptions of this document. And Junos implements an implicit deny - https://kb.juniper.net/InfoCenter/index?page=content&id=KB20778&actp=METADATA.